General Service Development
This page aims to guide developers on how to develop General Service type extension packages.
DANGER
When extension web pages (including Web Mini Programs and General Services ) are open, physical buttons and shortcuts on the industrial teaching pendant will be disabled.
To enable shortcuts in your extension, please refer to: Enable Shortcuts
About General Services
General Service extensions are used to implement complex backend functionality.
Unlike Easy Services, General Service extensions require developers to focus on service configuration, interface design, request processing, data storage, etc., making the development process more complex, but also providing more flexibility and extensibility.
General Service Features
- Powerful functionality: Can handle more complex business logic and data operations.
- Flexible and extensible: Can extend or modify service functionality according to business needs.
- Supports external interaction: Can interact with databases, external APIs, or other systems.
- Requires manual configuration: Compared to Easy Services, developers need to configure HTTP interfaces, request processing, routing, etc.
Startup Requirements
When a general service plugin starts, the plugin system assigns it a port number and passes this value to the process through the environment variable PORT .
The extension system will then check whether the extension process has successfully bound and is listening on that port.
Required Conditions
- Regardless of whether your service uses HTTP, TCP, gRPC, WebSocket, or a custom binary protocol, it must bind and listen on the port specified by PORT.
- The system will automatically assign a port number within the 6100-6199 range. If you need to use multiple ports, you must dynamically obtain available ports within this range yourself.
- Otherwise, the system will be unable to detect the listening state of the port and will treat the extension startup as failed after a timeout (default: 60 seconds).
Creating General Service Extension Package
In this demonstration, we will create a General Service type extension. The function of this extension is to provide a weather query interface.
TIP
WeatherService in the following text is the name of the General Service extension we are about to create.
Step 1: Create Extension Folder
First, we need to create a basic extension folder that contains a config.json configuration file and a Python file.
You can create it manually from scratch or modify the template in the "demo" directory in the extension development package repository.
Directory structure:
- WeatherService
- config.json
- app.py
import os
import logging
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
import requests
# Dynamically get port number, general service ports are automatically assigned
PORT = os.getenv("PORT", 8000)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.DEBUG,
format='%(asctime)s - %(filename)s:%(lineno)d - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
)
app = FastAPI()
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["*"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"]
)
@app.get("/weather")
async def get_weather():
"""
Get weather for specified city
:return: City weather information
"""
# Build query URL
url = f'http://t.weather.sojson.com/api/weather/city/101030100'
try:
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise HTTPException(status_code=response.status_code, detail="Failed to request weather data")
# The returned data is a string, return directly to client
weather_info = response.json()
return {"weather": weather_info}
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Failed to request external weather service")
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=int(PORT)){
"name": "WeatherService",
"type": "generalService",
"scriptLang": "python",
"description": "Weather Service",
"version": "0.1",
"entry": "app.py"
}Step 2: Package and Install
For extension packaging, please refer to Packaging and Installation
Step 3: Call the Interface
- Like easy services, general services need to be activated before they can be used.
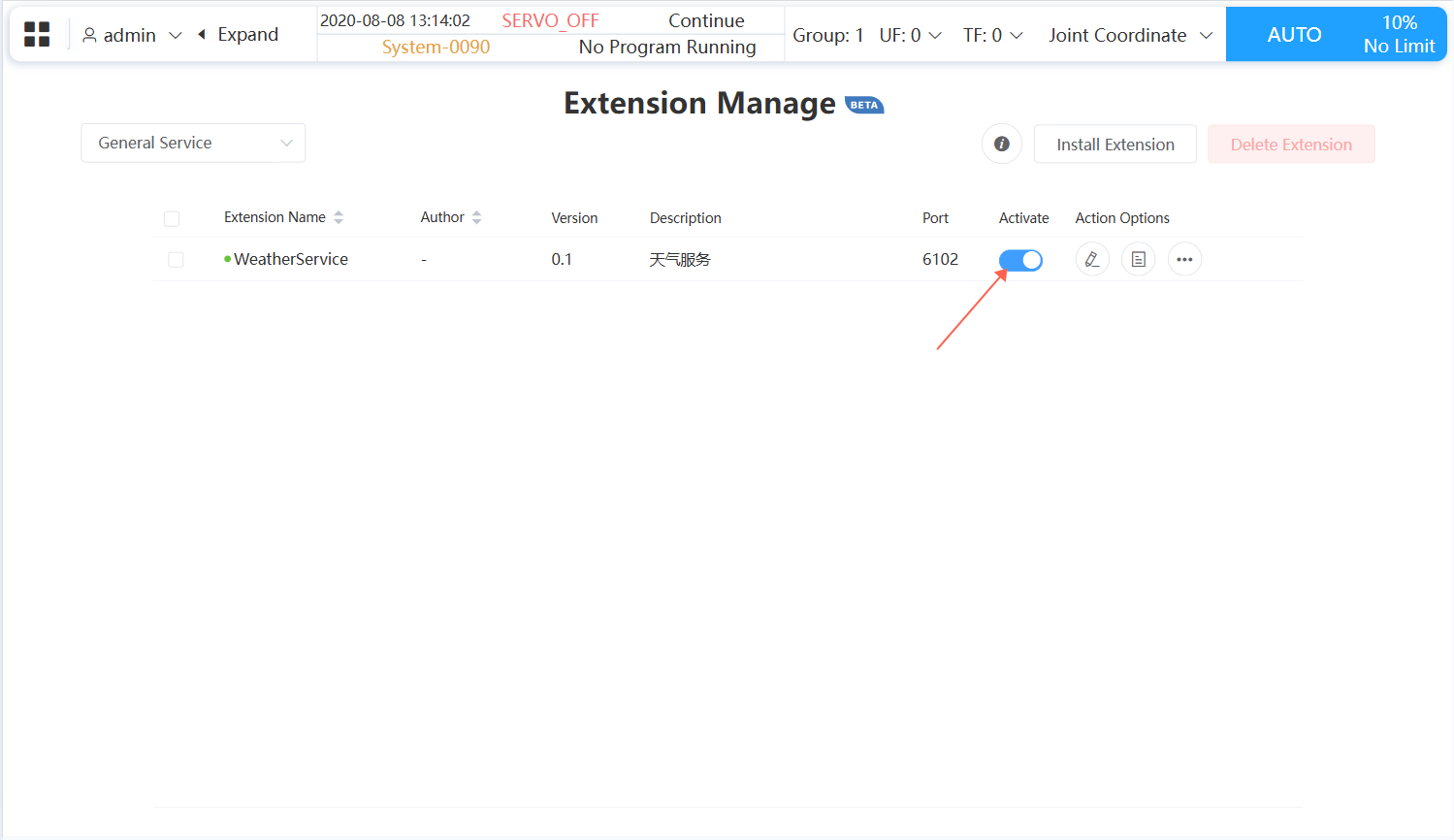
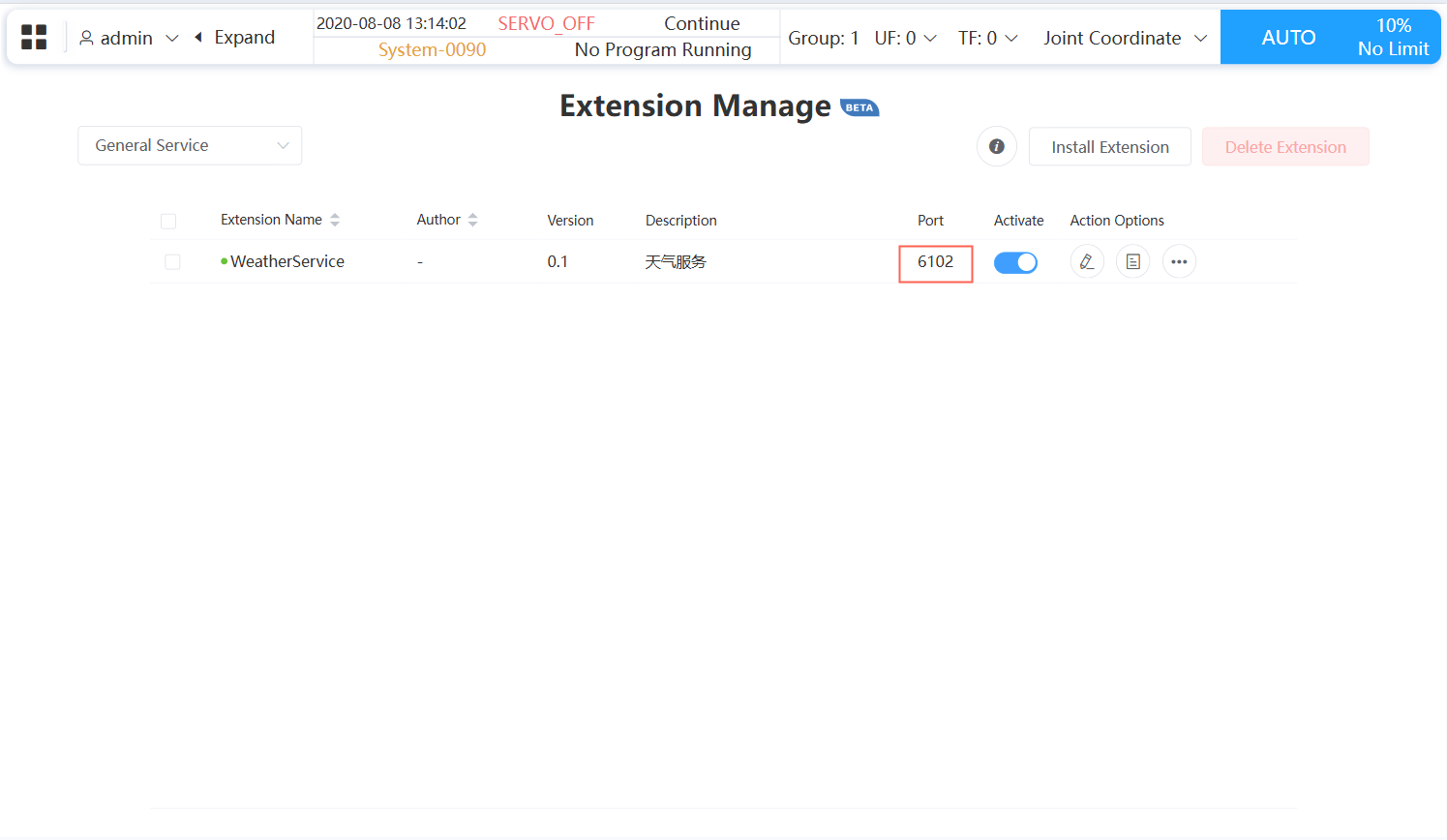
- After activation, you will see the service port number:
TIP
Once a General Service is started, it will preferentially be assigned the port number it occupied during the last startup when restarting (if this port number is already occupied, a new port number will be randomly assigned).
- Call this interface in other programs:
http://10.27.1.254:6100/weatherFor example, you can call this API using the Python requests package:
import requests
url = "http://10.27.1.254:6100/weather"
try:
response = requests.get(url)
# Check if the request was successful
if response.status_code == 200:
result = response.json()
print("Weather information:")
print(result)
else:
print(f"Request failed, status code: {response.status_code}")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print("An error occurred during the request:", e)