Target Following Demo
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the AgileBot robot for target following tasks.
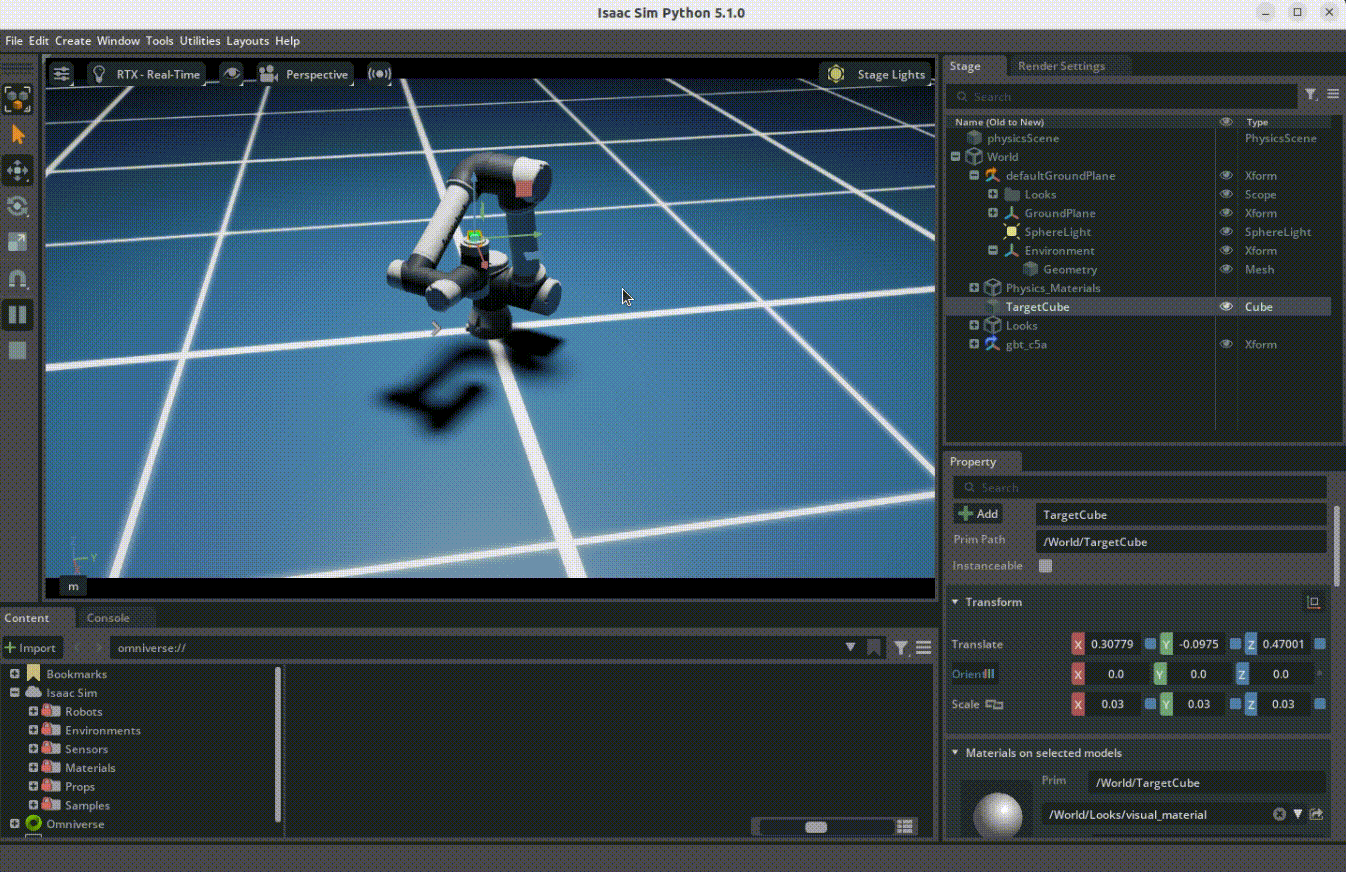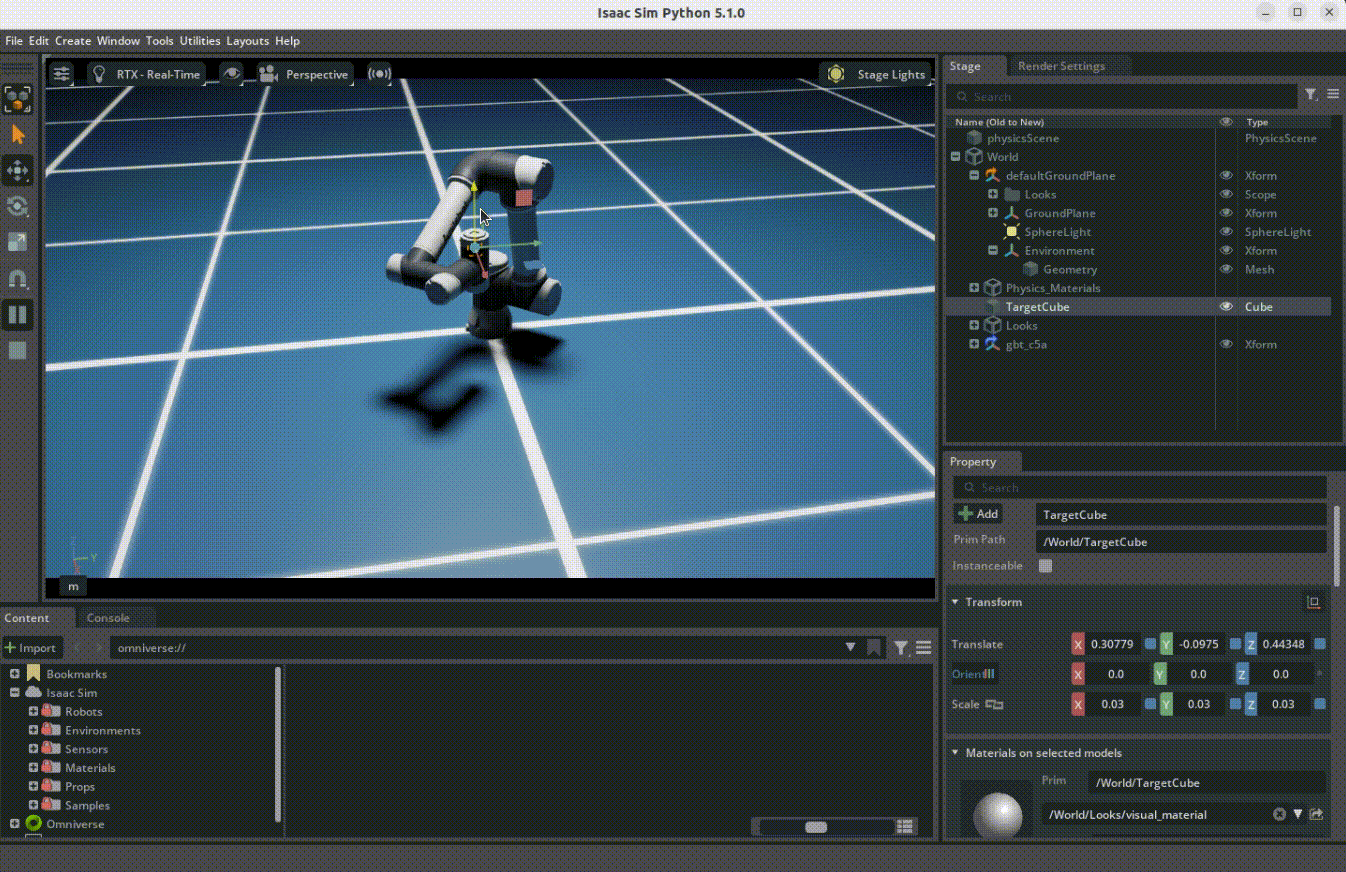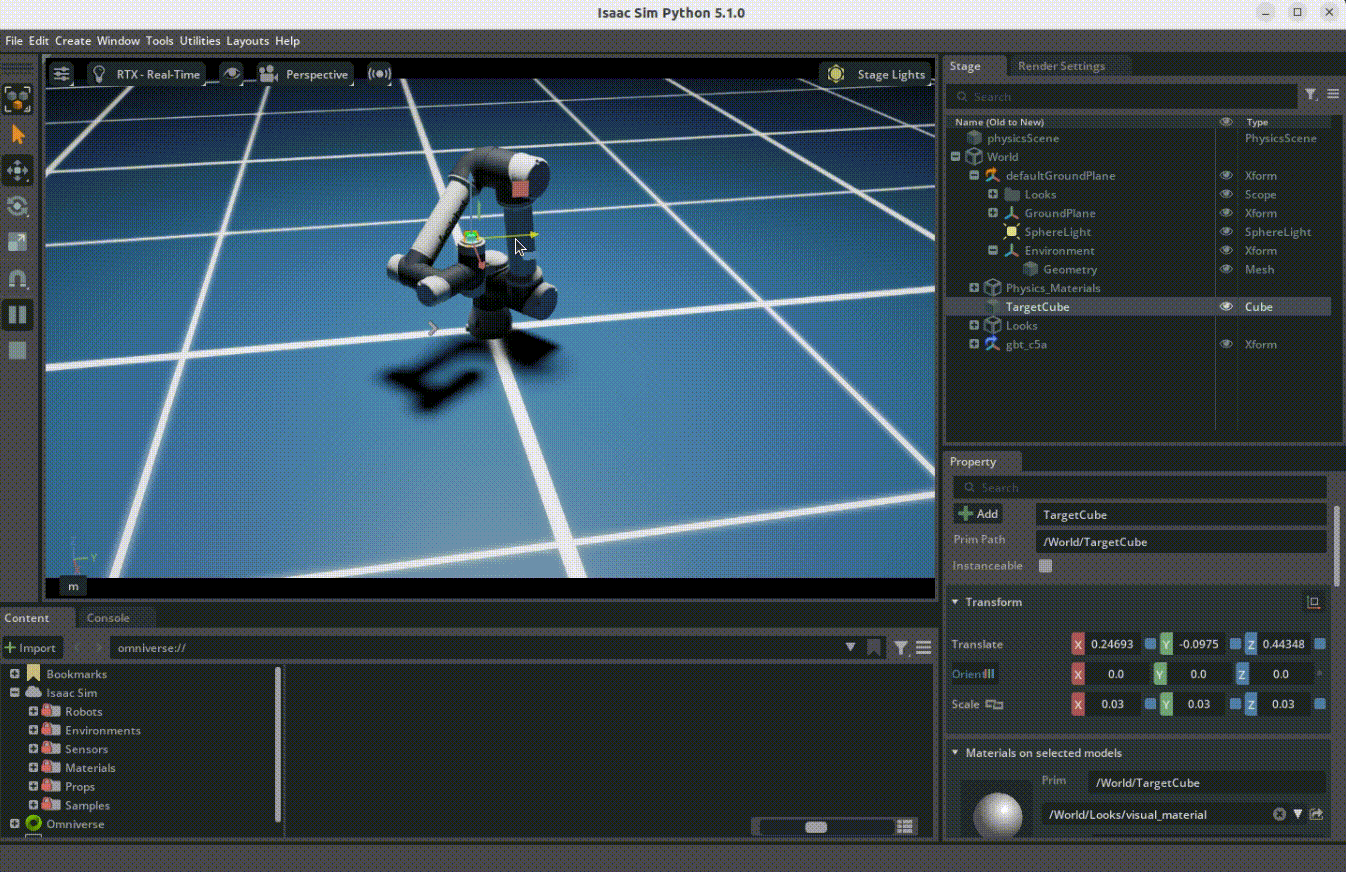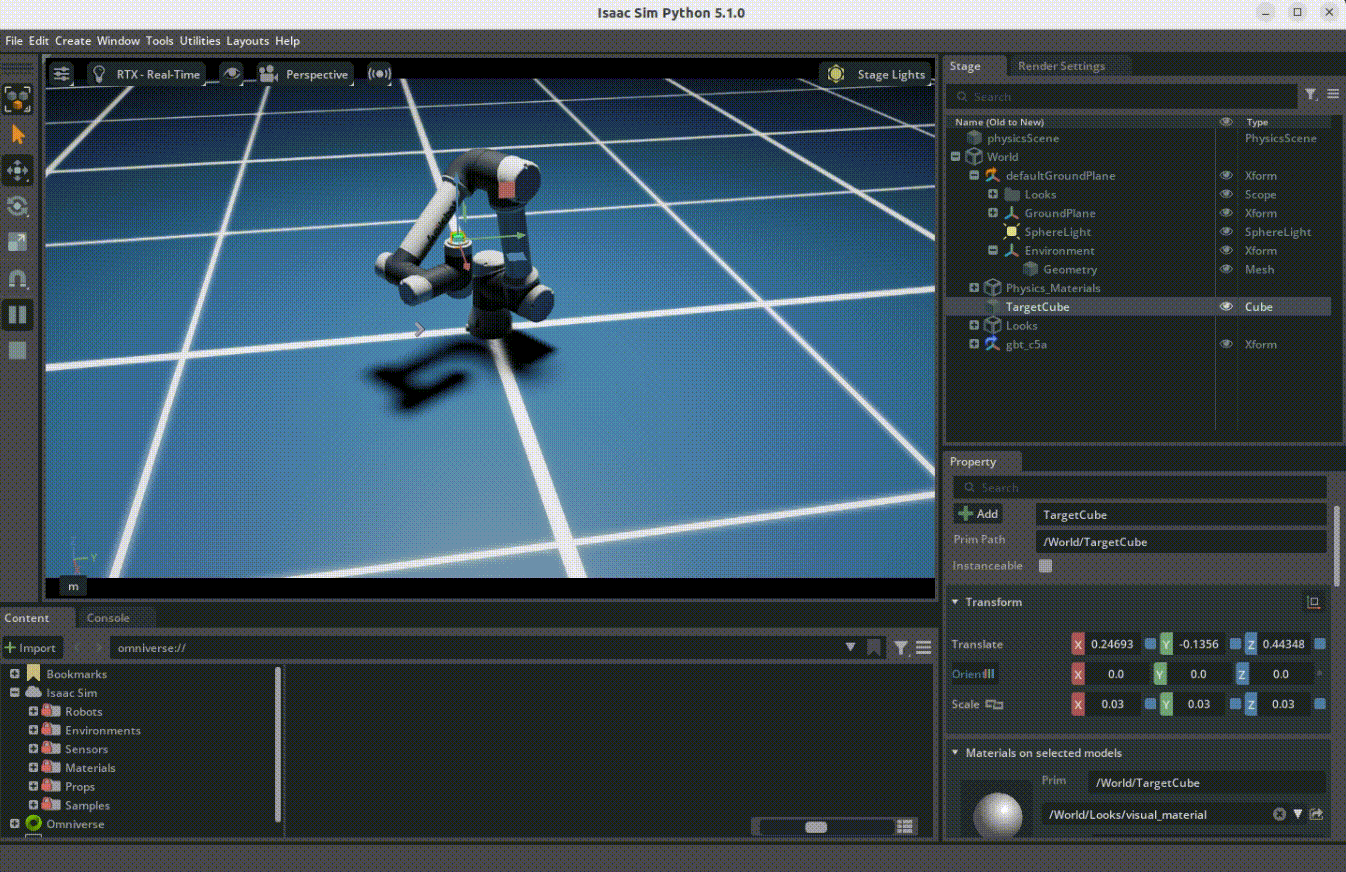
Overview
The target following demo shows how robots can use the RMPflow motion policy to follow moving targets. This demo uses Isaac Sim's motion generation framework.
Prerequisites
- Completed Isaac Sim Environment Configuration
- Completed Visualizing AgileBot Robot Models
Running the Demo
Using the Demo Script Provided by the Project
cd agilebot_isaac_sim
python agilebot_integration/demos/follow_target.pyDemo Description
RMPflow Motion Policy
RMPflow (Robot Motion Policy Flow) is a framework for robot motion planning that generates smooth, safe trajectories by combining multiple motion policies.
Target Following Algorithm
- Target Detection: Detect the position of the target object
- Trajectory Planning: Use RMPflow to compute trajectories from current position to target position
- Motion Execution: Control robot joints to follow the planned trajectory
- Obstacle Avoidance: Avoid obstacles during movement
Configuration Parameters
Motion Policy Configuration
Motion policy configuration files are located in the project source directory agilebot_integration/motion_policy_configs/Agilebot/gbt_c7a/ .
According to the Environment Configuration Guide, you need to copy the configuration files to the IsaacSim installation directory:
cp -r agilebot_integration/motion_policy_configs/Agilebot \
~/isaacsim/exts/isaacsim.robot_motion.motion_generation/motion_policy_configs/After copying, the full configuration file path is:
~/isaacsim/exts/isaacsim.robot_motion.motion_generation/motion_policy_configs/Agilebot/gbt_c7a/Main configuration parameters (reference RMPflow Official Tuning Guide):
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
c-space_target_rmp/metric_scalar | C-space target RMP weight | 1-100 |
c-space_target_rmp/robust_position_term_thresh | Robust position term threshold | Adjust based on joint count |
target_rmp/metric_scalar | Target RMP weight | Adjust based on task |
target_rmp/min_metric_alpha | Minimum metric alpha | 0 or non-zero |
target_rmp/metric_alpha_length_scale | Metric alpha length scale | 100000 |
target_rmp/proximity_metric_boost_length_scalar | Proximity metric boost length scalar | 1 |
target_rmp/max_metric_scalar | Maximum metric scalar | Large value |
target_rmp/accel_p_gain | Acceleration P gain | Adjust based on task |
target_rmp/accel_d_gain | Acceleration D gain | Adjust based on task |
target_rmp/accel_norm_eps | Acceleration normalization epsilon | Adjust based on task |
collision_rmp/metric_scalar | Collision avoidance RMP weight | Comparable to target_rmp |
damping_rmp/inertia | Damping RMP inertia | 0 |
Tuning Suggestions
- C-space Target RMP: Set
metric_scalarin the range 1-100, which sets the global scale of all RMPs - Target RMP: Set a large
max_metric_scalarto make it dominant; C-space target will operate in the nullspace of the target RMP - Collision Avoidance RMP: Set weight comparable to
target_rmp/max_metric_scalar - Directional Term: Set
min_metric_alphato a non-zero value and adjustmetric_alpha_length_scalefor good behavior
FAQ
Q: Robot cannot reach target position
A: Check if the target position is within the robot's workspace. If the target position is outside the workspace, the robot cannot reach it. Adjust target_tolerance parameter to suit task requirements.
Q: Motion trajectory is not smooth
A: Adjust RMPflow configuration parameters, especially:
- Check the gain values of
target_rmp/accel_p_gainandtarget_rmp/accel_d_gain - Ensure
metric_scalarvalues are within a reasonable range
Q: Robot collides with obstacles
A: Increase collision_rmp/metric_scalar parameter value to ensure the collision avoidance RMP has sufficient weight to avoid obstacles.
Q: How to tune from scratch
A: Reference the official tuning process:
- Turn off all RMPs (set
metric_scalarto 0) - Set all inertia terms to 0
- Re-enable RMPs one by one: c-space_target_rmp → target_rmp → collision_rmp → axis_target_rmp